CVD vs HPHT Diamonds: Which is the Better Manmade Diamond Manufacturing Process?

According to a report by The Brainy Insight, the global lab-grown diamond market has surged to unprecedented heights, reaching a staggering value of $10.8 billion in 2022. The industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.7% from 2023 to 2032 to reach $20.6 billion. This monumental figure not only underscores the exponential growth of the lab grown diamond and jewelry industry but also heralds a transformative era in the world of gemstones. In the wake of this paradigm shift, wholesalers, retailers, and consumers alike are confronted with a monumental choice between two groundbreaking manufacturing processes: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and High-Pressure High-Temperature (HPHT). As the demand for sustainable and ethically sourced diamonds continues to soar, understanding the intricacies of these cutting-edge technologies becomes paramount. These methods have revolutionised the diamond industry, offering an alternative to natural diamonds with comparable quality and characteristics.
CVD Diamond Production
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a cutting-edge technology used to grow lab-grown diamonds. In this process, a diamond seed is placed in a vacuum chamber filled with a hydrocarbon gas such as methane. Microwave energy is then applied to heat the gas into a plasma, causing carbon atoms to separate and bond with the diamond seed plate. This results in the growth of diamond layers over days or weeks.
Advantages of CVD Diamonds
- Precision in Manufacturing: CVD technology allows for precise control over the growth process, resulting in diamonds with consistent quality and characteristics.
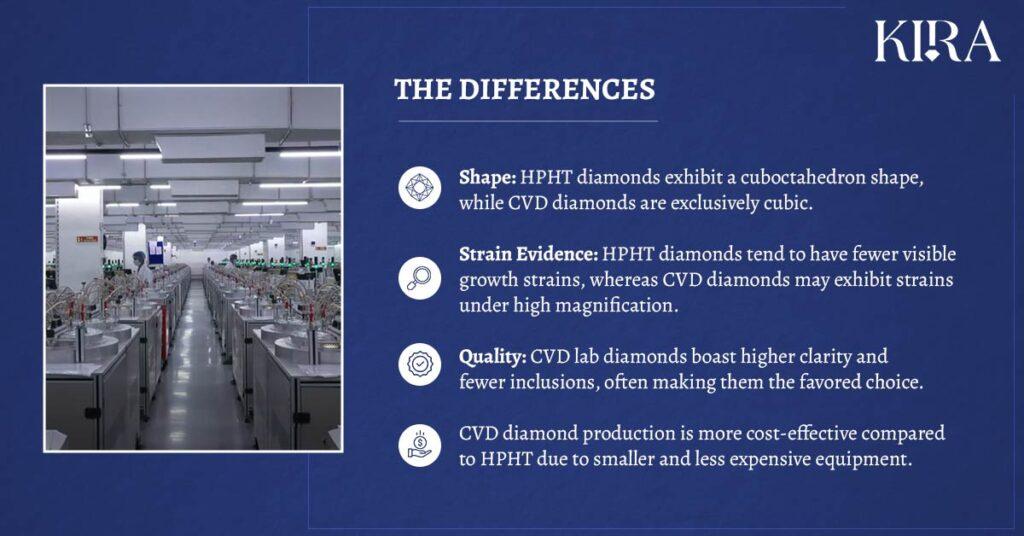
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to HPHT, CVD diamond production is more cost-effective due to the smaller and less expensive equipment required.
- Environmental Benefits: CVD reactors consume less energy and are more environmentally friendly compared to HPHT presses, making them a sustainable choice for diamond manufacturing.
HPHT Diamond Manufacturing
High-pressure High-temperature (HPHT) is another method used to create lab-grown diamonds. This process involves subjecting a diamond seed to immense pressure (around 1 million PSI) and high temperatures (exceeding 1500 degrees Celsius) similar to those found below the Earth’s crust. The pressure and temperature conditions cause carbon atoms to bond and form diamond layers around the seed.
Key Features of HPHT Diamonds
- Natural-Like Characteristics: HPHT diamonds exhibit characteristics similar to natural diamonds, including high transparency and purity levels.
- Unique Colouration: HPHT diamonds can exhibit unique colouration due to boron or nitrogen impurities, adding to their aesthetic appeal.
- Diverse Applications: HPHT diamonds have applications in both jewelry and industrial sectors due to their high quality and durability.
Quality of CVD and HPHT Diamonds
Dislocation Density
- CVD diamond shows a comparatively low dislocation density compared to HPHT diamond due to the high-quality HPHT diamond substrate.
- Dislocation density in CVD diamond is observed to be below 1 nm on both sides.
Impurity Concentration
Substitutional nitrogen (Ns) impurity concentration:
- CVD diamond: 2.1 ppb
- HPHT diamond: Several tens ppb
The concentration of Ns impurities in CVD diamond is significantly lower compared to HPHT diamond. Detector Energy Resolution:
- HPHT diamond detector: 2.04%
- CVD diamond detector: 0.86%
The energy resolution of CVD diamond detectors is significantly better compared to HPHT diamond detectors. Charge Collection Efficiency (CCE) Under positive voltage:
- HPHT diamond detector: 38.11%
- CVD diamond detector: 86.65%
The CCE of CVD diamond detectors is significantly higher compared to HPHT diamond detectors under positive voltage.
Cost Factors
In terms of cost, CVD and HPHT diamonds vary based on production methods, equipment requirements, and market demand.
Comparative Cost Analysis
- CVD Diamonds: CVD diamond production is more cost-effective compared to HPHT due to smaller and less expensive equipment.
- HPHT Diamonds: HPHT diamond production requires large and expensive presses, leading to higher production costs compared to CVD.
 Get Your Kira Mobile Apps Now On The App Store & Google Play!
Get Your Kira Mobile Apps Now On The App Store & Google Play!
Market Trends
In the current market, both CVD and HPHT diamonds have their own share of demand and popularity.
Current Market Trends for CVD Diamonds
- Growing Demand: CVD diamonds are experiencing a surge in demand due to their cost-effectiveness and sustainable manufacturing process. The Brainy Insight report also states that of the 10.8 billion market valuation of LGD, 52% was occupied by the CVD segment.
- Certification: Certified lab grown diamonds, especially those certified by reputable organisations like the International Gemological Institute (IGI), are gaining traction among consumers.
Future Projections for CVD and HPHT Diamonds
- CVD Growth: The CVD diamond market is expected to continue growing as technology advances and production processes become more efficient.
- HPHT Demand: HPHT diamonds may remain popular in niche markets, especially among consumers seeking unique colourations.
Applications and Uses
Both CVD and HPHT diamonds find applications in various industries, including jewelry, electronics, and industrial sectors.
Industrial Applications of CVD Diamonds
- Jewelry: CVD diamonds are used in jewelry due to their precision, natural-like properties and low cost of production.
- Electronics: CVD diamonds are used in various electronic applications, including semiconductors and thermal management systems, due to their high thermal conductivity and electrical properties.
- Cutting Tools: CVD diamonds are also used in cutting tools and abrasives, offering superior hardness and wear resistance compared to natural diamonds.
Jewelry and Industrial Uses of HPHT Diamonds
- Jewelry: HPHT diamonds are popular in fine jewelry due to their natural-like characteristics and unique colourations.
- Industrial Tools: HPHT diamonds find applications in industrial tools and equipment, including drill bits and saw blades, owing to their hardness and durability.
Scalability and Production Volume
When it comes to scalability and production volume, CVD has an advantage over HPHT.
Scalability of CVD Diamond Production
- Efficiency: CVD diamond production is highly scalable, allowing for efficient mass production of diamonds to meet market demands.
- Flexibility: CVD reactors can be easily scaled up or down based on production requirements, offering flexibility to manufacturers.
Production Volume Capabilities of HPHT
- Limited Scalability: HPHT diamond production is less scalable compared to CVD, as it requires large and expensive presses that are less flexible in terms of production volume.
- Specialised Applications: HPHT diamonds are often produced in smaller volumes for specialised applications, limiting their scalability in mass production scenarios.
Looking for loose diamonds?
Looking for loose diamonds? Discover Kira, the world’s largest CVD diamond producer, offering over 250,000 certified diamond stones ranging from 0.18 to 10+ carats, all sourced from our state-of-the-art Surat facility. Specializing in stunning fancy-colored diamonds—yellow, pink, blue, and green—in a variety of shapes, including Round, Oval, Radiant, Emerald, Pear, Princess, and Marquise. With 3000+ CVD machines and a reliable global delivery service, we can fulfil orders of any size. Join our established end-to-end supply chain and experience the quality and variety that Kira has to offer.
Technology Comparison
In terms of technology, CVD and HPHT processes have distinct differences and ongoing advancements.
Technical Differences Between CVD and HPHT Processes
- Growth Environment: CVD diamonds are grown in a vacuum chamber using hydrocarbon gas, while HPHT diamonds are grown under high pressure and temperature conditions similar to those found below the Earth’s crust.
- Control and Precision: CVD technology allows for precise control over the growth process, resulting in consistent quality and characteristics, while HPHT technology provides less precision.
Innovations and Advancements in Each Technology
- CVD Advancements: Ongoing advancements in CVD technology are focused on improving efficiency, reducing production costs, and enhancing diamond quality through process optimisation and equipment innovation.
- HPHT Innovations: HPHT technology continues to evolve with advancements in press design, temperature and pressure control, and growth chamber optimisation, leading to higher quality and larger diamond production.
Recommendations for Wholesale Buyers
For wholesale diamond buyers, partnering with reputable lab grown diamond companies is essential. Conducting comparative cost analyses and evaluating quality factors such as purity, clarity, and market demand will aid in making informed decisions. Additionally, staying abreast of market trends and technological advancements will ensure alignment with evolving consumer preferences and industry standards. At Kira Jewels, we are leading the way in this monumental change in the diamond and the diamond jewelry industry. As the largest grower of CVD lab-grown diamonds globally, we acknowledge the significance of providing eco-conscious and ethically obtained diamonds to our clientele. Our dedication to sustainability goes beyond mere rhetoric; it is deeply embedded in our operations and methodologies. 💎 Biggest Manufacturing Facility
- Spread across 1,000,000 sq.ft.
- Powered by a 25+ MW solar plant
💎 Dedicated to Innovation and Woman Empowerment
- 8000+ artisans
- Run by a 70% female workforce
💎 Leading the Charge in Production Capacity
- 250,000+ diamond stones inventory
- 0.18 to 10+ CTS diamond stone range
Check out our inventory to get a closer look at our range of offerings.
Future Outlook for CVD and HPHT Diamonds
The future outlook for lab-grown diamonds is optimistic, with both CVD and HPHT technologies poised for growth and innovation in the lab-grown diamond industry. However, CVD continues to gain significant traction across the world due to higher purity and quality control, better color & clarity, rapid size and production speed, and more cost-effectiveness as compared to their counterparts. Kira remains the prime manufacturer of CVD diamonds with our extensive commitment to lab-grown diamond manufacturing. Learn more about our diamond manufacturing practices here.